Github Scraper
Tool designed to scrape and analyze repositories from GitHub based on customizable search criteria.
Github Scraper Repository
Features
- Customizable Search: Filter repositories by programming language, associated tools/technologies (e.g., Docker, React, TensorFlow), and star ratings.
- Date Filtering: Retrieve repositories updated within a specific time range (e.g., last 6 months, 1 year).
- Rate Limit Handling: Automatically handles GitHub API rate limits to ensure uninterrupted scraping.
- CLI and GUI Interfaces: Offers both command-line and graphical user interfaces for flexibility.
- Metadata Extraction: Fetches repository metadata, including the latest commit date, owner details, and more.
- Retry Mechanism: Implements retry logic for failed API requests, ensuring robustness.
How It Works
The GitHub Scanner uses the GitHub REST API to query repositories based on user-defined parameters. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of its operation:
- Input Parameters: The user specifies search criteria such as programming language, tools, star range, and date range.
- API Requests: The tool sends requests to the GitHub API to fetch matching repositories.
- Data Processing: Extracts relevant metadata, such as repository name, owner, latest commit date, and star count.
- Output: Displays the results in a structured format (e.g., CLI output or GUI table).
The scraper also includes a retry mechanism to handle rate limits and transient errors gracefully.
Code Structure
The codebase is organized into modular components for maintainability and scalability:
- API Interaction:
make_api_request: Handles API calls with retry logic and rate limit management.check_rate_limit: Fetches and displays the current rate limit status.
- Search Functions:
search_repositories: Queries GitHub for repositories based on search criteria.get_repository_metadata: Retrieves detailed metadata for a specific repository.
- Utility Functions:
is_within_date_range: Filters repositories based on the latest commit date.get_latest_commit_date: Fetches the most recent commit date for a repository.
- User Interface:
- CLI: Provides a text-based interface for input and output.
- GUI: Offers a graphical interface for ease of use.
Interface
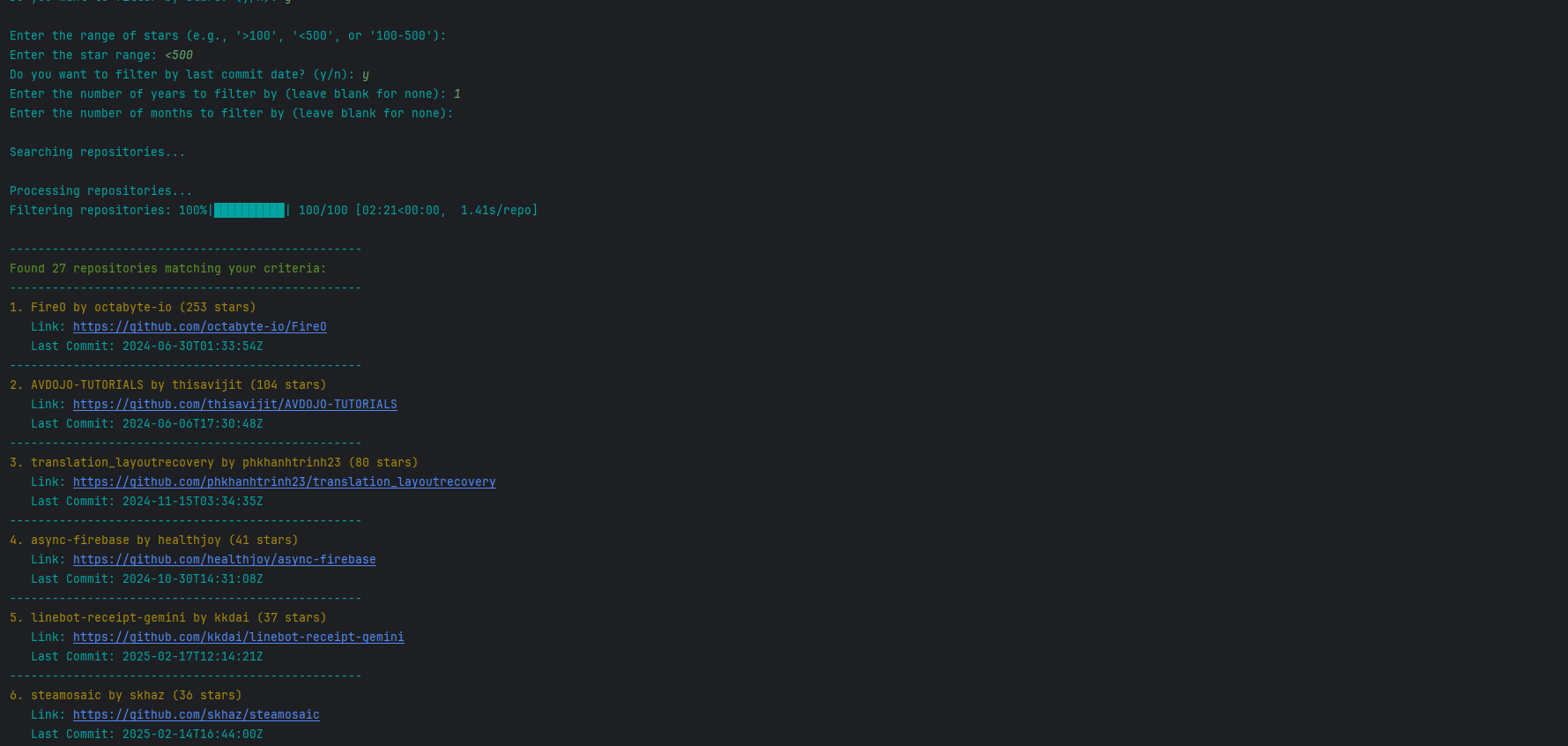
CLI Version
The CLI version provides a straightforward, text-based interface for users who prefer simplicity and speed. Below is an example of the CLI interface:
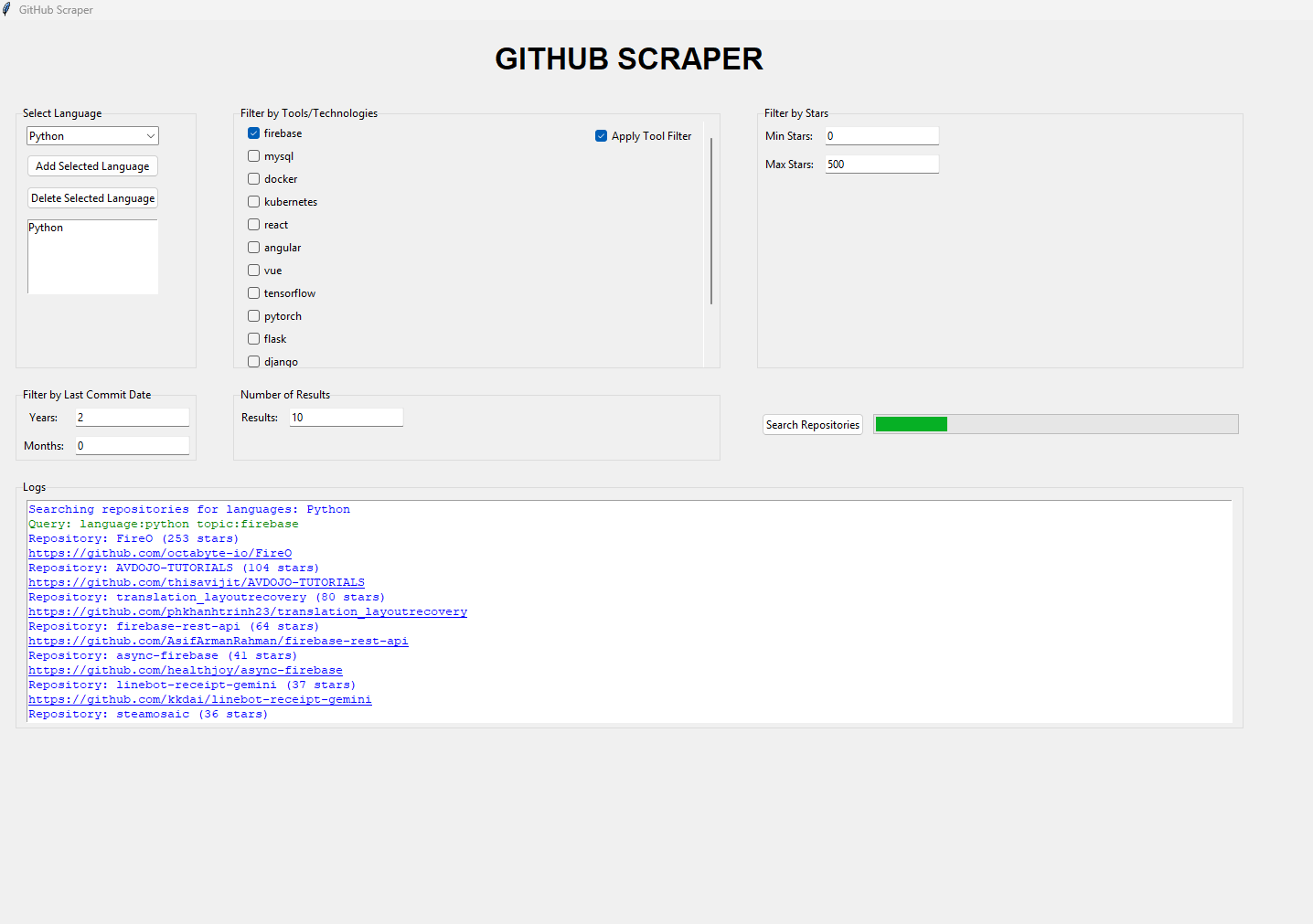
GUI Version
The GUI version offers a more interactive experience with dropdown menus, checkboxes, and visual feedback. Users can select programming languages, filter by tools/technologies, specify star ranges, and set date filters through intuitive controls. A progress bar provides real-time updates during the scraping process, while a log area displays clickable links to the discovered repositories.
Here’s a preview of the GUI interface:
Creating a GitHub Token
To use the GitHub Scanner, you need to generate a personal access token:
- Go to your GitHub Account Settings.
- Navigate to Developer Settings → Personal Access Tokens → Tokens (classic).
- Click Generate New Token and select Generate New Token (classic).
- Select the necessary scopes (e.g.,
repo,read:org). - Copy the generated token and paste it into the script where indicated (
YOUR_GITHUB_TOKEN_HERE).
Limitations
- Rate Limits: GitHub imposes strict rate limits on unauthenticated and authenticated API requests. While the scraper handles these limits, excessive queries may still lead to temporary blocks.
- Search Complexity: Complex queries with multiple filters may take longer to process due to API constraints.
- Data Completeness: The scraper relies on GitHub’s API, which may not expose all repository details.
Future Enhancements
- Advanced Filters: Add support for filtering by license type, repository size, or contributor count.
- Export Options: Allow users to export results in various formats (e.g., CSV, JSON, Excel).
- Parallel Processing: Implement multi-threading to speed up large-scale queries.
- Web Interface: Develop a web-based dashboard for remote access and collaboration.
- Machine Learning Integration: Use ML models to recommend repositories based on user preferences.
Ethical Considerations
- Respect Rate Limits: Always adhere to GitHub’s API usage policies to avoid overloading their servers.
- Data Privacy: Ensure that scraped data is used responsibly and does not violate any privacy agreements.
- Attribution: Properly credit repository owners when using their data for research or analysis.
Tips and Tricks
- Optimize Queries: Use specific keywords and filters to narrow down results and reduce API calls.
- Monitor Rate Limits: Regularly check your rate limit status to avoid unexpected interruptions.
- Use Tokens Wisely: Authenticate with a personal access token to increase your rate limit allowance.
- Batch Processing: For large datasets, consider breaking queries into smaller batches to stay within rate limits.
Extra Insights
- The scraper supports multiple programming languages and tools, making it versatile for various use cases.
- By analyzing the latest commit dates, users can identify actively maintained repositories.
- Combining star ratings with other filters helps prioritize high-quality projects.